tar는 Tape ARchiver의 약자로 여러 개의 파일을 하나의 파일로 묶거나 묶은 파일을 다시 여러 개의 파일로 풀 때 사용하는 명령어입니다.


흔히 linux에서 tar로 압축한다는 표현을 사용하는데, 정확히 말하자면 tar 자체는 파일 압축을 수행하지는 않습니다.
단지 파일을 하나의 파일로 묶는 기능만 하기 때문에 tar 파일로 생성했다고 해서 용량이 줄어들지는 않습니다.
하지만 이후에 gzip 또는 bzip2 방식을 같이 사용할 수 있게 되어 tar 명령어로도 파일 압축을 할 수 있게 됩니다.
정리하자면 tar 자체는 파일 압축을 수행하지는 않지만, tar + (gzip | bzip2)와 같이 사용하면 tar 명령어로도 파일 압축을 수행할 수 있습니다.
확장자
일반적으로는 tar 명령어로 생성한 파일의 확장자는 ".tar"입니다.
그리고 gzip, bzip2와 같이 사용하여 생성한 파일의 경우 ".tar.gz" 또는 ".tar.bz2"로 파일 확장자를 지정하는데, 이를 합쳐 ".tgz" 또는 ".tb2", ".tbz", ".tbz2" 등으로 지정하기도 합니다.

사용법
linux에서 tar 명령어를 살펴보면 아래와 같이 정말 많은 옵션들이 있는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
옵션들이 너무 많지만 전부 다 사용하는 것은 아니기 때문에 이 중에서 가장 많이 사용하는 Main Operation mode와 Compression options에 대해서 정리해 보도록 하겠습니다.
user@ubuntu:~/data/kafka-logs/__consumer_offsets-0$ tar --help
Usage: tar [OPTION...] [FILE]...
GNU 'tar' saves many files together into a single tape or disk archive, and can
restore individual files from the archive.
Examples:
tar -cf archive.tar foo bar # Create archive.tar from files foo and bar.
tar -tvf archive.tar # List all files in archive.tar verbosely.
tar -xf archive.tar # Extract all files from archive.tar.
Local file name selection:
--add-file=FILE add given FILE to the archive (useful if its name
starts with a dash)
-C, --directory=DIR change to directory DIR
--exclude=PATTERN exclude files, given as a PATTERN
--exclude-backups exclude backup and lock files
--exclude-caches exclude contents of directories containing
CACHEDIR.TAG, except for the tag file itself
--exclude-caches-all exclude directories containing CACHEDIR.TAG
--exclude-caches-under exclude everything under directories containing
CACHEDIR.TAG
--exclude-ignore=FILE read exclude patterns for each directory from
FILE, if it exists
--exclude-ignore-recursive=FILE
read exclude patterns for each directory and its
subdirectories from FILE, if it exists
--exclude-tag=FILE exclude contents of directories containing FILE,
except for FILE itself
--exclude-tag-all=FILE exclude directories containing FILE
--exclude-tag-under=FILE exclude everything under directories
containing FILE
--exclude-vcs exclude version control system directories
--exclude-vcs-ignores read exclude patterns from the VCS ignore files
--no-null disable the effect of the previous --null option
--no-recursion avoid descending automatically in directories
--no-unquote do not unquote input file or member names
--no-verbatim-files-from -T treats file names starting with dash as
options (default)
--null -T reads null-terminated names; implies
--verbatim-files-from
--recursion recurse into directories (default)
-T, --files-from=FILE get names to extract or create from FILE
--unquote unquote input file or member names (default)
--verbatim-files-from -T reads file names verbatim (no escape or option
handling)
-X, --exclude-from=FILE exclude patterns listed in FILE
File name matching options (affect both exclude and include patterns):
--anchored patterns match file name start
--ignore-case ignore case
--no-anchored patterns match after any '/' (default for
exclusion)
--no-ignore-case case sensitive matching (default)
--no-wildcards verbatim string matching
--no-wildcards-match-slash wildcards do not match '/'
--wildcards use wildcards (default for exclusion)
--wildcards-match-slash wildcards match '/' (default for exclusion)
Main operation mode:
-A, --catenate, --concatenate append tar files to an archive
-c, --create create a new archive
-d, --diff, --compare find differences between archive and file system
--delete delete from the archive (not on mag tapes!)
-r, --append append files to the end of an archive
-t, --list list the contents of an archive
--test-label test the archive volume label and exit
-u, --update only append files newer than copy in archive
-x, --extract, --get extract files from an archive
Operation modifiers:
--check-device check device numbers when creating incremental
archives (default)
-g, --listed-incremental=FILE handle new GNU-format incremental backup
-G, --incremental handle old GNU-format incremental backup
--hole-detection=TYPE technique to detect holes
--ignore-failed-read do not exit with nonzero on unreadable files
--level=NUMBER dump level for created listed-incremental archive
-n, --seek archive is seekable
--no-check-device do not check device numbers when creating
incremental archives
--no-seek archive is not seekable
--occurrence[=NUMBER] process only the NUMBERth occurrence of each file
in the archive; this option is valid only in
conjunction with one of the subcommands --delete,
--diff, --extract or --list and when a list of
files is given either on the command line or via
the -T option; NUMBER defaults to 1
--sparse-version=MAJOR[.MINOR]
set version of the sparse format to use (implies
--sparse)
-S, --sparse handle sparse files efficiently
Overwrite control:
-k, --keep-old-files don't replace existing files when extracting,
treat them as errors
--keep-directory-symlink preserve existing symlinks to directories when
extracting
--keep-newer-files don't replace existing files that are newer than
their archive copies
--no-overwrite-dir preserve metadata of existing directories
--one-top-level[=DIR] create a subdirectory to avoid having loose files
extracted
--overwrite overwrite existing files when extracting
--overwrite-dir overwrite metadata of existing directories when
extracting (default)
--recursive-unlink empty hierarchies prior to extracting directory
--remove-files remove files after adding them to the archive
--skip-old-files don't replace existing files when extracting,
silently skip over them
-U, --unlink-first remove each file prior to extracting over it
-W, --verify attempt to verify the archive after writing it
Select output stream:
--ignore-command-error ignore exit codes of children
--no-ignore-command-error treat non-zero exit codes of children as
error
-O, --to-stdout extract files to standard output
--to-command=COMMAND pipe extracted files to another program
Handling of file attributes:
--atime-preserve[=METHOD] preserve access times on dumped files, either
by restoring the times after reading
(METHOD='replace'; default) or by not setting the
times in the first place (METHOD='system')
--clamp-mtime only set time when the file is more recent than
what was given with --mtime
--delay-directory-restore delay setting modification times and
permissions of extracted directories until the end
of extraction
--group=NAME force NAME as group for added files
--group-map=FILE use FILE to map file owner GIDs and names
--mode=CHANGES force (symbolic) mode CHANGES for added files
--mtime=DATE-OR-FILE set mtime for added files from DATE-OR-FILE
-m, --touch don't extract file modified time
--no-delay-directory-restore
cancel the effect of --delay-directory-restore
option
--no-same-owner extract files as yourself (default for ordinary
users)
--no-same-permissions apply the user's umask when extracting permissions
from the archive (default for ordinary users)
--numeric-owner always use numbers for user/group names
--owner=NAME force NAME as owner for added files
--owner-map=FILE use FILE to map file owner UIDs and names
-p, --preserve-permissions, --same-permissions
extract information about file permissions
(default for superuser)
--same-owner try extracting files with the same ownership as
exists in the archive (default for superuser)
-s, --preserve-order, --same-order
member arguments are listed in the same order as
the files in the archive
--sort=ORDER directory sorting order: none (default), name or
inode
Handling of extended file attributes:
--acls Enable the POSIX ACLs support
--no-acls Disable the POSIX ACLs support
--no-selinux Disable the SELinux context support
--no-xattrs Disable extended attributes support
--selinux Enable the SELinux context support
--xattrs Enable extended attributes support
--xattrs-exclude=MASK specify the exclude pattern for xattr keys
--xattrs-include=MASK specify the include pattern for xattr keys
Device selection and switching:
-f, --file=ARCHIVE use archive file or device ARCHIVE
--force-local archive file is local even if it has a colon
-F, --info-script=NAME, --new-volume-script=NAME
run script at end of each tape (implies -M)
-L, --tape-length=NUMBER change tape after writing NUMBER x 1024 bytes
-M, --multi-volume create/list/extract multi-volume archive
--rmt-command=COMMAND use given rmt COMMAND instead of rmt
--rsh-command=COMMAND use remote COMMAND instead of rsh
--volno-file=FILE use/update the volume number in FILE
Device blocking:
-b, --blocking-factor=BLOCKS BLOCKS x 512 bytes per record
-B, --read-full-records reblock as we read (for 4.2BSD pipes)
-i, --ignore-zeros ignore zeroed blocks in archive (means EOF)
--record-size=NUMBER NUMBER of bytes per record, multiple of 512
Archive format selection:
-H, --format=FORMAT create archive of the given format
FORMAT is one of the following:
gnu GNU tar 1.13.x format
oldgnu GNU format as per tar <= 1.12
pax POSIX 1003.1-2001 (pax) format
posix same as pax
ustar POSIX 1003.1-1988 (ustar) format
v7 old V7 tar format
--old-archive, --portability
same as --format=v7
--pax-option=keyword[[:]=value][,keyword[[:]=value]]...
control pax keywords
--posix same as --format=posix
-V, --label=TEXT create archive with volume name TEXT; at
list/extract time, use TEXT as a globbing pattern
for volume name
Compression options:
-a, --auto-compress use archive suffix to determine the compression
program
-I, --use-compress-program=PROG
filter through PROG (must accept -d)
-j, --bzip2 filter the archive through bzip2
-J, --xz filter the archive through xz
--lzip filter the archive through lzip
--lzma filter the archive through xz
--lzop filter the archive through lzop
--no-auto-compress do not use archive suffix to determine the
compression program
-z, --gzip, --gunzip, --ungzip filter the archive through gzip
--zstd filter the archive through zstd
-Z, --compress, --uncompress filter the archive through compress
Local file selection:
--backup[=CONTROL] backup before removal, choose version CONTROL
-h, --dereference follow symlinks; archive and dump the files they
point to
--hard-dereference follow hard links; archive and dump the files they
refer to
-K, --starting-file=MEMBER-NAME
begin at member MEMBER-NAME when reading the
archive
--newer-mtime=DATE compare date and time when data changed only
-N, --newer=DATE-OR-FILE, --after-date=DATE-OR-FILE
only store files newer than DATE-OR-FILE
--one-file-system stay in local file system when creating archive
-P, --absolute-names don't strip leading '/'s from file names
--suffix=STRING backup before removal, override usual suffix ('~'
unless overridden by environment variable
SIMPLE_BACKUP_SUFFIX)
File name transformations:
--strip-components=NUMBER strip NUMBER leading components from file
names on extraction
--transform=EXPRESSION, --xform=EXPRESSION
use sed replace EXPRESSION to transform file
names
Informative output:
--checkpoint[=NUMBER] display progress messages every NUMBERth record
(default 10)
--checkpoint-action=ACTION execute ACTION on each checkpoint
--full-time print file time to its full resolution
--index-file=FILE send verbose output to FILE
-l, --check-links print a message if not all links are dumped
--no-quote-chars=STRING disable quoting for characters from STRING
--quote-chars=STRING additionally quote characters from STRING
--quoting-style=STYLE set name quoting style; see below for valid STYLE
values
-R, --block-number show block number within archive with each message
--show-defaults show tar defaults
--show-omitted-dirs when listing or extracting, list each directory
that does not match search criteria
--show-snapshot-field-ranges
show valid ranges for snapshot-file fields
--show-transformed-names, --show-stored-names
show file or archive names after transformation
--totals[=SIGNAL] print total bytes after processing the archive;
with an argument - print total bytes when this
SIGNAL is delivered; Allowed signals are: SIGHUP,
SIGQUIT, SIGINT, SIGUSR1 and SIGUSR2; the names
without SIG prefix are also accepted
--utc print file modification times in UTC
-v, --verbose verbosely list files processed
--warning=KEYWORD warning control
-w, --interactive, --confirmation
ask for confirmation for every action
Compatibility options:
-o when creating, same as --old-archive; when
extracting, same as --no-same-owner
Other options:
-?, --help give this help list
--restrict disable use of some potentially harmful options
--usage give a short usage message
--version print program version
Mandatory or optional arguments to long options are also mandatory or optional
for any corresponding short options.
The backup suffix is '~', unless set with --suffix or SIMPLE_BACKUP_SUFFIX.
The version control may be set with --backup or VERSION_CONTROL, values are:
none, off never make backups
t, numbered make numbered backups
nil, existing numbered if numbered backups exist, simple otherwise
never, simple always make simple backups
Valid arguments for the --quoting-style option are:
literal
shell
shell-always
shell-escape
shell-escape-always
c
c-maybe
escape
locale
clocale
*This* tar defaults to:
--format=gnu -f- -b20 --quoting-style=escape --rmt-command=/usr/sbin/rmt
--rsh-command=/usr/bin/rsh
Main operation mode와 Compression options
Main operation mode:
-A, --catenate, --concatenate append tar files to an archive
-c, --create create a new archive
-d, --diff, --compare find differences between archive and file system
--delete delete from the archive (not on mag tapes!)
-r, --append append files to the end of an archive
-t, --list list the contents of an archive
--test-label test the archive volume label and exit
-u, --update only append files newer than copy in archive
-x, --extract, --get extract files from an archive
Compression options:
-a, --auto-compress use archive suffix to determine the compression
program
-I, --use-compress-program=PROG
filter through PROG (must accept -d)
-j, --bzip2 filter the archive through bzip2
-J, --xz filter the archive through xz
--lzip filter the archive through lzip
--lzma filter the archive through xz
--lzop filter the archive through lzop
--no-auto-compress do not use archive suffix to determine the
compression program
-z, --gzip, --gunzip, --ungzip filter the archive through gzip
--zstd filter the archive through zstd
-Z, --compress, --uncompress filter the archive through compres

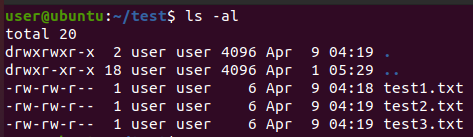
묶음 & 묶음 해제
-c: 지정한 파일(들)을 tar 파일로 묶습니다.
-x: 지정한 tar 파일의 묶음을 해제합니다.
📢 tar 자체는 압축의 기능이 없기 때문에 여기선 '묶음'이라는 표현을 사용했습니다.
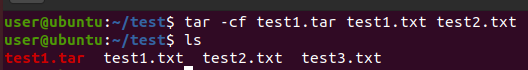
tar -cf [tar 명] [file1] [file2] [file3...]
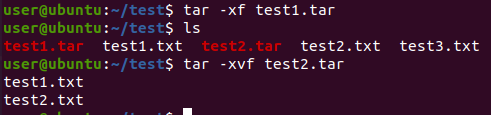
-x 옵션은 묶음(압축) 해제 시 사용하며, -v 옵션과 함께 사용할 경우 압축 해제되는 파일들을 출력합니다.
출력
-t: tar 안에 있는 파일(들)을 목록으로 표시합니다.
-v: 압축 & 압축 해제 과정을 상세한 메시지로 출력합니다.
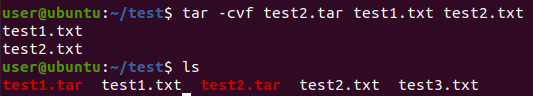
-v 옵션을 사용하면 압축되는 파일들을 출력합니다.
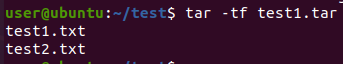
-t 옵션을 사용하면 해당 tar 안에 있는 파일 목록을 출력합니다.
압축
-z: tar를 gzip으로 압축허거나, -x과 같이 사용하는 경우 해당 파일이 gzip으로 압축되었음을 가리킵니다.
-j: tar를 bzip2로 압축하거나, -x과 같이 사용하는 경우 해당 파일을 bzip2로 압축 해제합니다.
-J: tar를 xz로 압축하거나, -x과 같이 사용하는 경우 해당 파일을 xz로 압축 해제합니다.
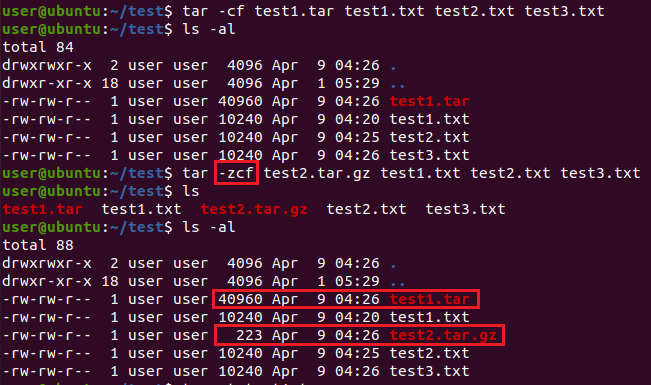
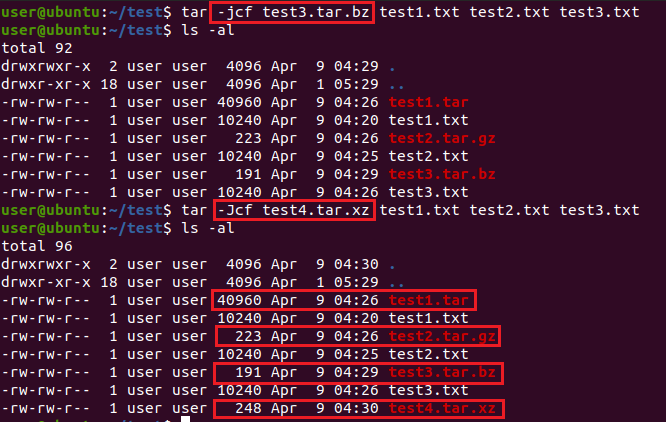
압축 옵션 없이 tar 파일을 생성하면 묶은 파일들의 용량이 모두 더해진 용량이 되고, 압축 옵션을 추가하게 될 경우 해당 압축 알고리즘에 의해 압축이 진행되어 용량이 크게 줄어든 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
압축 해제의 경우 -c 대신 -x 옵션을 사용하면 됩니다. 사용한 옵션과 해당 파일이 서로 다른 압축 형식일 경우 에러 메시지가 출력됩니다.
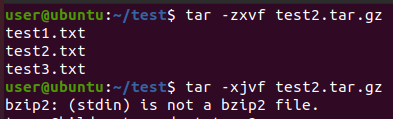
압축된 파일 내용 보기
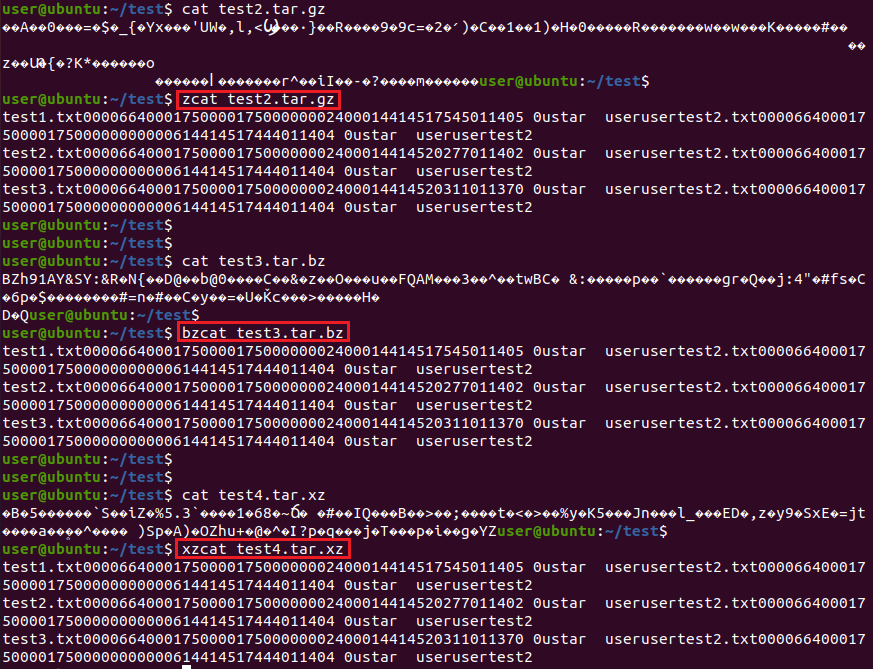
압축된 파일의 내용을 cat, vi 명령어로 확인하게 될 경우 압축된 이상한 문자들이 출력되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
압축된 파일의 내용을 보기 위해서는 아래와 같이 각 압축 형식에 따른 제공되는 명령어를 사용하면 됩니다.
zcat: gzip 압축 파일 내용 보기
bzcat: bzip2 압축 파일 내용 보기
xzcat: xz 압축 파일 내용 보기
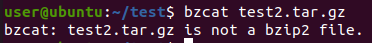
압축 형식에 맞는 명령어를 사용하지 않을 경우 에러 메시지가 출력됩니다.
참고 자료
- https://recipes4dev.tistory.com/146
- https://namu.wiki/w/tar
- [따배L] 05. Archiving and Compression (1)
- [따배L] 05. Archiving and Compression (2)
'Linux' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Redirection (0) | 2023.05.07 |
|---|---|
| 파일 유형 (File Type) (0) | 2023.04.02 |
| Linux 기본 명령어 - ls (0) | 2023.04.02 |
| Linux 기본 명령어 - mkdir & rmdir (0) | 2023.04.02 |
| Linux 기본 명령어 - cd (Change Directory) (0) | 2023.04.01 |




댓글